Marvel Comics is a comic book publisher founded in 1939 as Timely Publications and later began operating under the umbrella of Marvel Entertainment activity. It is known for creating characters such as Spider-Man, Iron Man, Captain America, Thor, Hulk, Black Widow and X-Men Men such as. With contributions from writers and artists like Stan Lee, Jack Kirby and Steve Ditko, Marvel Comics has produced content not only in comic books but also on cinema and digital media platforms, establishing a vast narrative universe. This universe systematically implemented the concept of a “shared universe” through interconnected character relationships.
Since the second half of the 20th century, Marvel Comics has been positioned as one of the prominent comic book publishers in the United States. It contributed to the diversification of superhero narratives and developed various approaches to storytelling within the comic industry. The publisher’s productions did not limit themselves to entertainment-focused content; they incorporated social, political and psychological themes into their narratives, appealing to diverse reader groups. Through storylines rooted in continuity and serialized fiction, Marvel Comics has produced works across different eras of the comic medium.
Founding and Historical Development
The foundations of Marvel Comics were laid by Timely Publications, established in 1939 by Martin Goodman. One of its earliest characters, the Human Torch, was closely associated with the science fiction and war themes of the era. In the 1950s, the publisher operated under the name Atlas Comics following a name change, and adopted the name Marvel Comics in 1961. During this transition, the Fantastic Four series developed by Stan Lee and Jack Kirby played a pivotal role in shifting the publisher’s approach to comic book storytelling.
One of its earliest issues, Marvel Comics #1 (1939), introduced the characters Human Torch and Sub-Mariner and stands as an early example of the comic book format. This publication is regarded as one of the foundational milestones in Marvel Comics’ development.
Founders and Creative Team
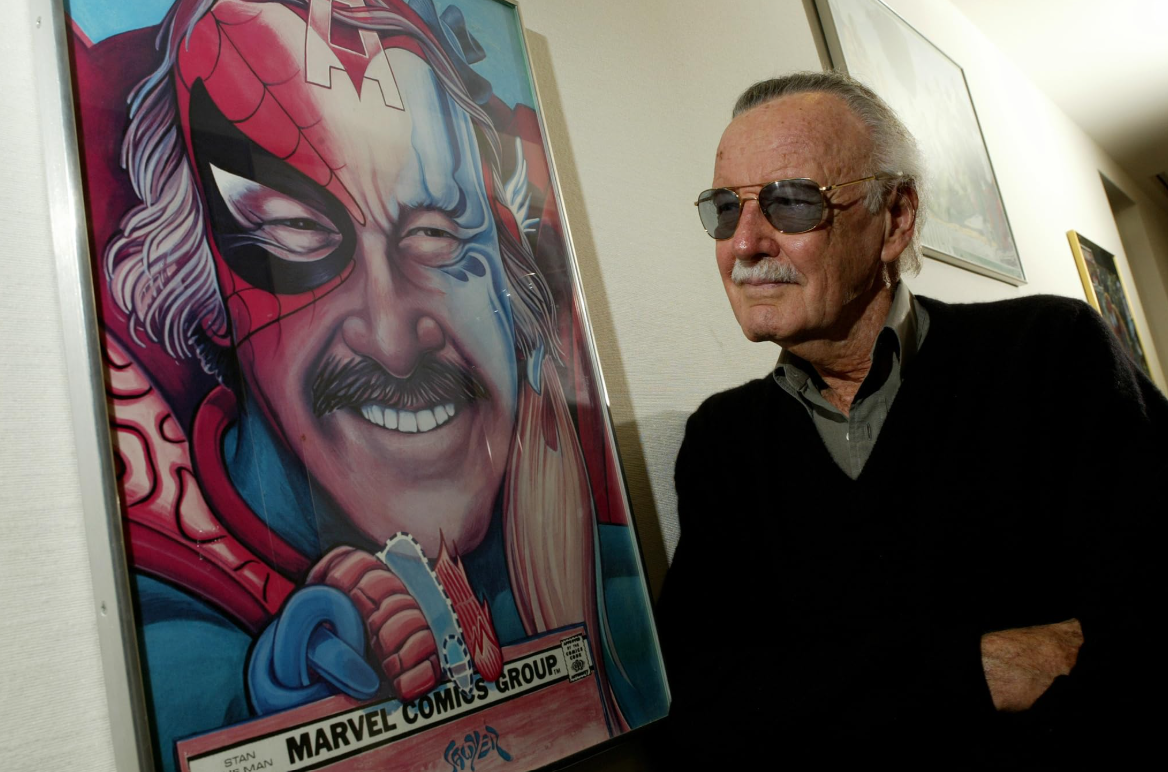

Stan Lee, Marvel Comics Group (Source:IMDb)
Within Marvel Comics, various writers and artists including Stan Lee, Jack Kirby, Steve Ditko, John Romita Sr. and Larry Lieber have contributed. These creators played a key role in developing character-driven storytelling. The creative model known as the “Marvel Method,” defined and implemented by Stan Lee, encouraged collaboration between writers and draws, granting artists greater creative input in narrative production. This method served as a model that supported the structural development of storytelling.
Publication Types and Thematic Depth
Marvel Comics’ publication range includes the following genres:

Superhero Example, Fantastic (Source: Marvel)
- Superhero
- Science Fiction
- Horror
- Adventure
- Fantasy
In addition to superhero narratives, Marvel Comics has produced publications across various genres such as science fiction, fantasy, fear and adventure. Its stories have addressed social issues, ethical dilemmas and individual psychology, making its works not merely entertaining but also open to intellectual reflection.
Excerpt from Marvel Comics (Source: Marvel)
Marvel characters have also appeared beyond comics on platforms such as cinema, television and digital media. These characters are not defined solely by physical power traits but also by human qualities such as vulnerability, indecision and moral conflict. This approach enabled Marvel to reach diverse age and sociocultural audiences.
Works published by Marvel Comics offer a broad spectrum of content targeting different age groups. In addition to superhero narratives, the publications exhibit variety through elements such as atmospheric world-building, character development and conflict dynamics.
Notable Publications and Characters
Marvel Comics’ 1961 publication Fantastic Four is regarded as one of the key turning points in the company’s genre and narrative evolution. Some of the prominent characters and series developed afterward are listed below:
- Spider-Man: A character narrative exploring the relationship between personal responsibility and the powers gained by a young man, Peter Parker, after being bitten by a radioactive spider.
- X-Men: A group narrative focusing on individuals marginalized by society due to genetic mutations, centered on themes of belonging and otherness.
- The Avengers: A superhero team narrative depicting collaboration among characters with diverse abilities and traits to confront a collective threat.
- Iron Man: A narrative portraying the personal transformation and ethical responsibilities of Tony Stark, who gains power through technology.
- Thor: A narrative rooted in Norse mythology, exploring the balance between divine and human dimensions.
- The Incredible Hulk: A structure centered on Bruce Banner’s internal conflicts and his transformation driven by rage following a scientific experiment.
- Black Panther: A narrative focusing on T’Challa, the leader of the fictional nation of Wakanda, addressing both technological advancement and the representation of traditional structures.
- Doctor Strange: Explores the struggles of Stephen Strange, a former surgeon who acquires mystical powers and navigates between alternate dimensions and realities.

Cover Art from Marvel Comics’ Spider-Man (Source: Marvel)
Word characters and series have been adapted beyond the comic book format into cinema, television, digital content and interactive media.
Marvel Comics features Spider-Man, a character first created in 1962 by Stan Lee and Steve Ditko, who battles evil while navigating life as an ordinary high school student endowed with superpowers.
Corporate Structure and Commercial Transformation
Marvel Comics operates under Marvel Entertainment. In 2009, it was acquired by The Walt Disney Company, becoming part of a multinational media and entertainment corporation. Following this acquisition, Marvel’s characters were systematically adapted into films, reaching wide audiences. Particularly after 2008, the Marvel brand demonstrated significant commercial growth in the film industry.
Cultural and Artistic Legacy
Marvel Comics has been evaluated not only within the context of the comic book industry but also as an object of cultural and artistic study. During the 1980s and 1990s, its character designs, narrative layers and graphic styles became subjects of various academic and critical analyses. Publications such as The Comics Journal explored the relationship between Marvel Comics’ aesthetic and institutional building, offering detailed analyses of its storytelling and production methods.
Global Impact
Marvel Comics’ influence has extended beyond comic book literature to fields such as cinema, digital media, consumer products and academic research. Through its superhero characters, it has addressed themes of identity, justice, individual responsibility and other related concepts, establishing connections with diverse sociocultural groups at multiple levels. The series developed within the Marvel Cinematic Universe (MCU) have achieved high box office revenues, expanding the superhero genre’s standing in the film industry. At the same time, Marvel representations have gained widespread presence in areas such as fashion, the toy industry and digital platforms, appearing in various forms within popular culture.
Marvel Comics occupies a prominent position as a publisher with a long-standing production history in the annals of comic books. The narrative structures developed by its creative teams have been linked to themes such as science, psychology and ethics, and its character designs have been reimagined across multiple media formats. In this context, Marvel Comics has established a multifaceted representational space in cultural production and has become a subject of interdisciplinary research.


